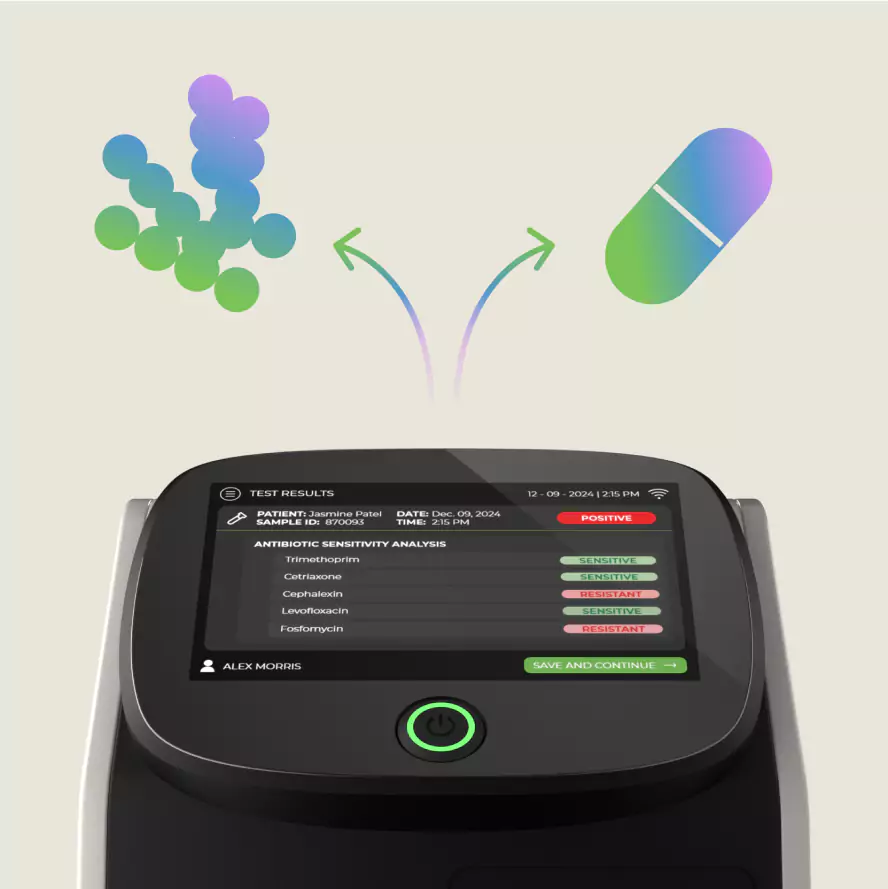
Our solution
Simplified diagnostic process
The JIDDU platform unlocks effortless diagnostics, simplifying complex tests with minimal training
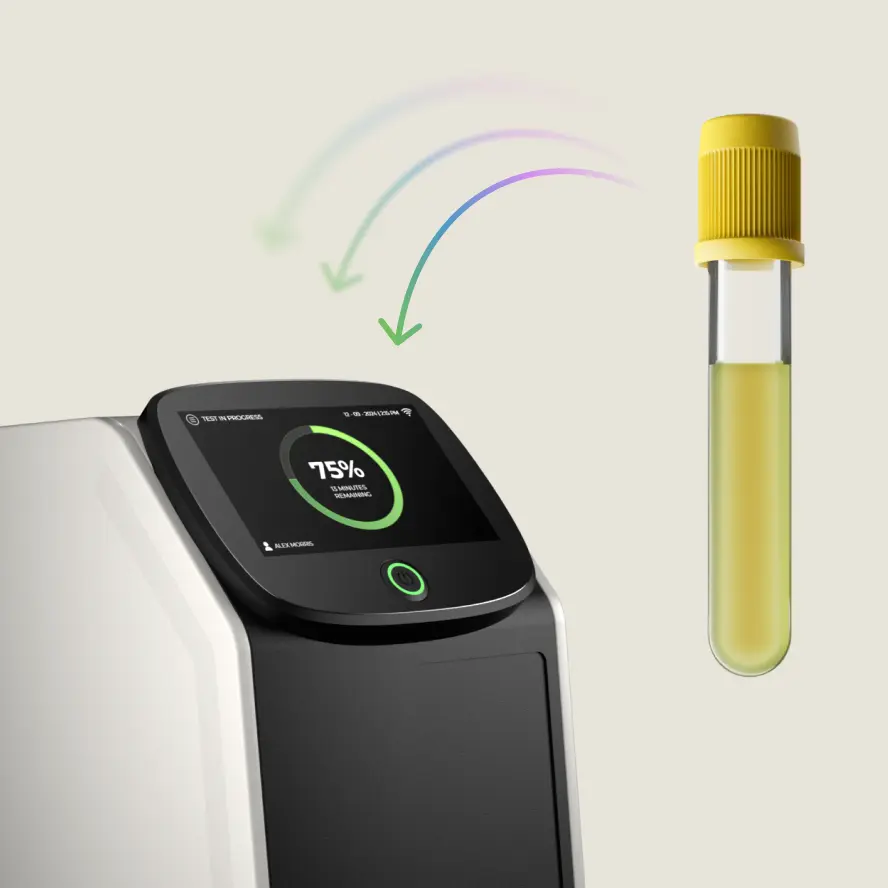
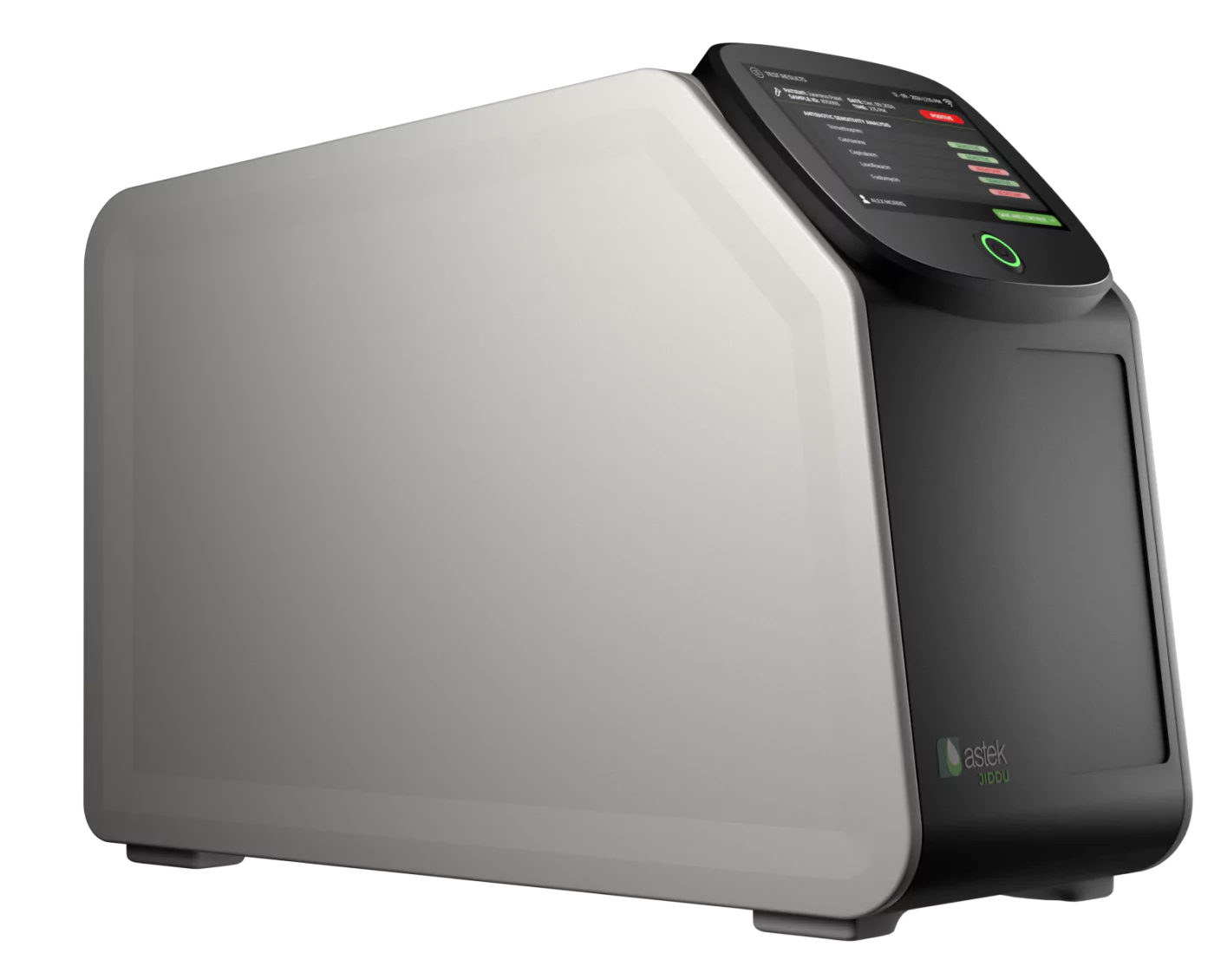
Our benchtop analyzer can identify the presence of a bacterial infection in urine and then perform antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) of the bacterium in one hour. This will inform physicians which antibiotics would be best to give to patients in a short period of time.
How it works
1
Place the sample into the cartidge
The sample is placed in a specialized microfluidic cartridge. The type of cartridge utilized varies with the sample type. Once attached, the cartridge is placed in the device and the automated testing process begins.
2
Bacteria from the sample is captured
Through an automated filtering process, the bacteria is captured from the sample. For the blood panel, this capturing process incorporates a step to eliminate hemoglobin from lysed blood cells.
3
Cultivation and antibiotic testing
The sample is subdivided into multiple channels, allowing it to be mixed with specified antibiotics, as well as have two control channels. Once divided and mixed, the sample channels are cultivated for 35 minutes in a conducive media.
4
Detection of bacteria presence
The sample channels mix with specified reagents before moving to an analysis chamber. After 15 minutes, the device is able to confirm the presence of bacteria in the sample as well as provide antibiotic sensitivity results for the pre-selected antibiotics.
1-Hour Results
Rapid UTI detection
Antibiotic sensitivity indication
Point-of-Care Testing
Actionable results
Expedited treatment
Ease of Use
Basic training requirement
Automated testing & Disposable cartridges
Technology overview
Metabolic activity detection
The technology behind the JIDDU platform translates metabolic activity into rapid and actionable results
Astek Diagnostics’ revolutionary diagnostic platform leverages microfluidics and is comprised of two distinct parts - a separation chamber and an analyzer. The bacteria is first isolated from urine in the separation chamber, and then metabolic activity is measured through an ultra-sensitive detector using fluorescent dye. This metabolic activity is used to determine antibiotic susceptibility.
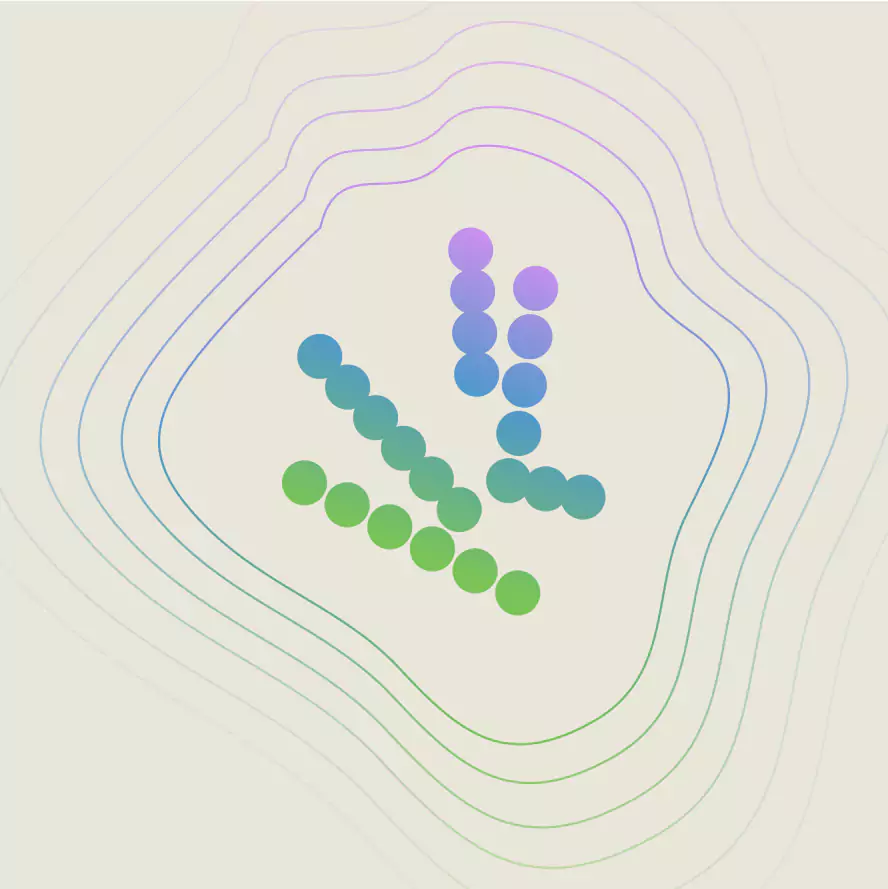
Metabolic activity example
Sample
TMP-SMX (Bactrim)
Ceftriaxone
Levofloxacin
Nitrofurantoin
Cephalexin
A high metabolic activity shows that an infection is present
TMP-SMX (marketed as Bactrim) is the go-to drug administered for UTIs
A decline in metabolic activity indicates the antibiotic is working